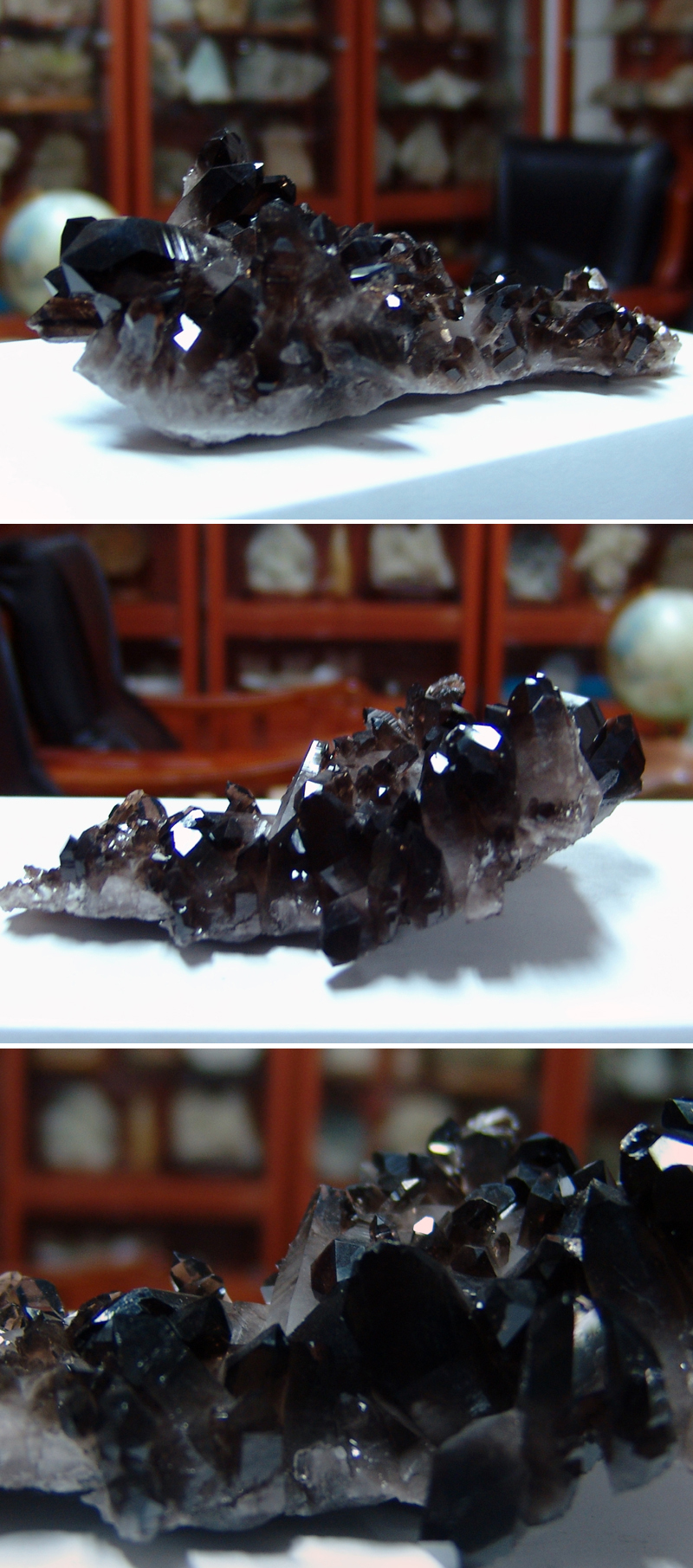
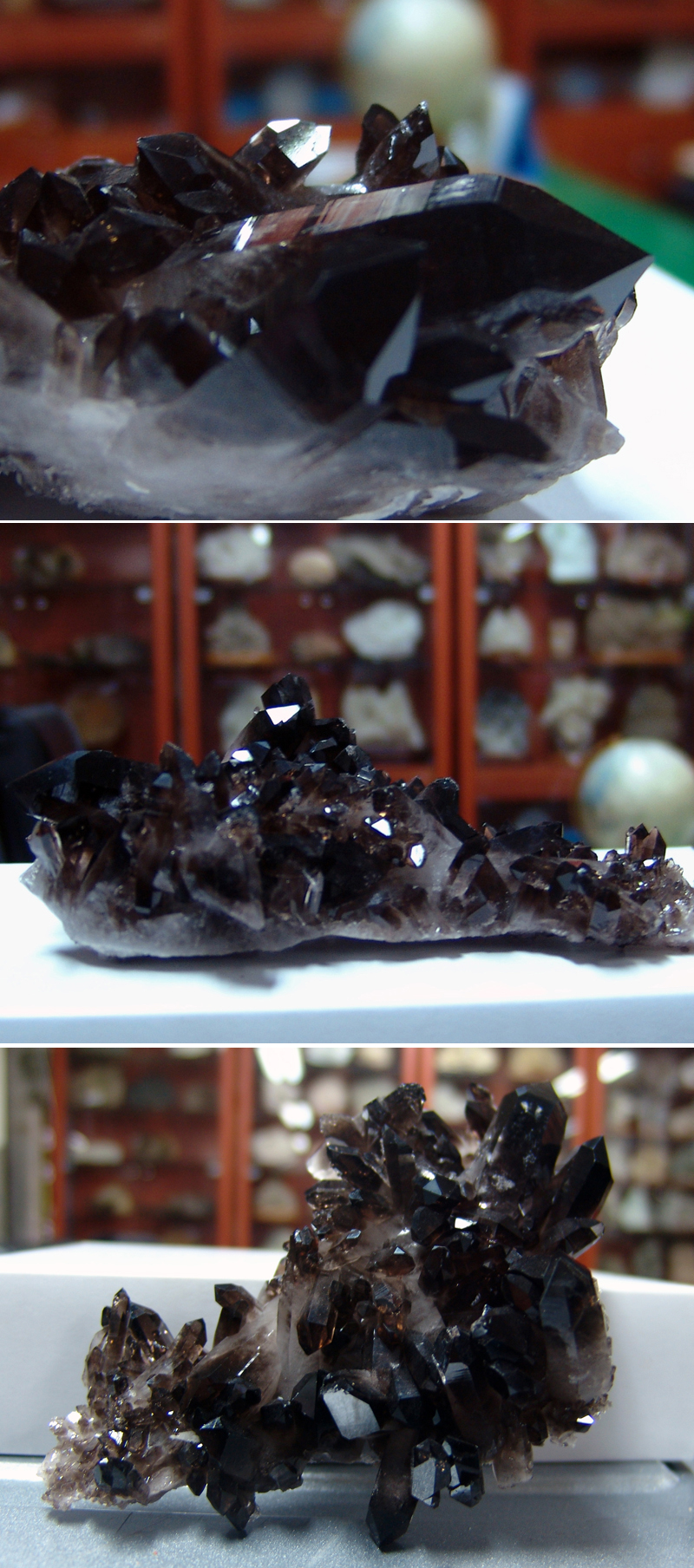
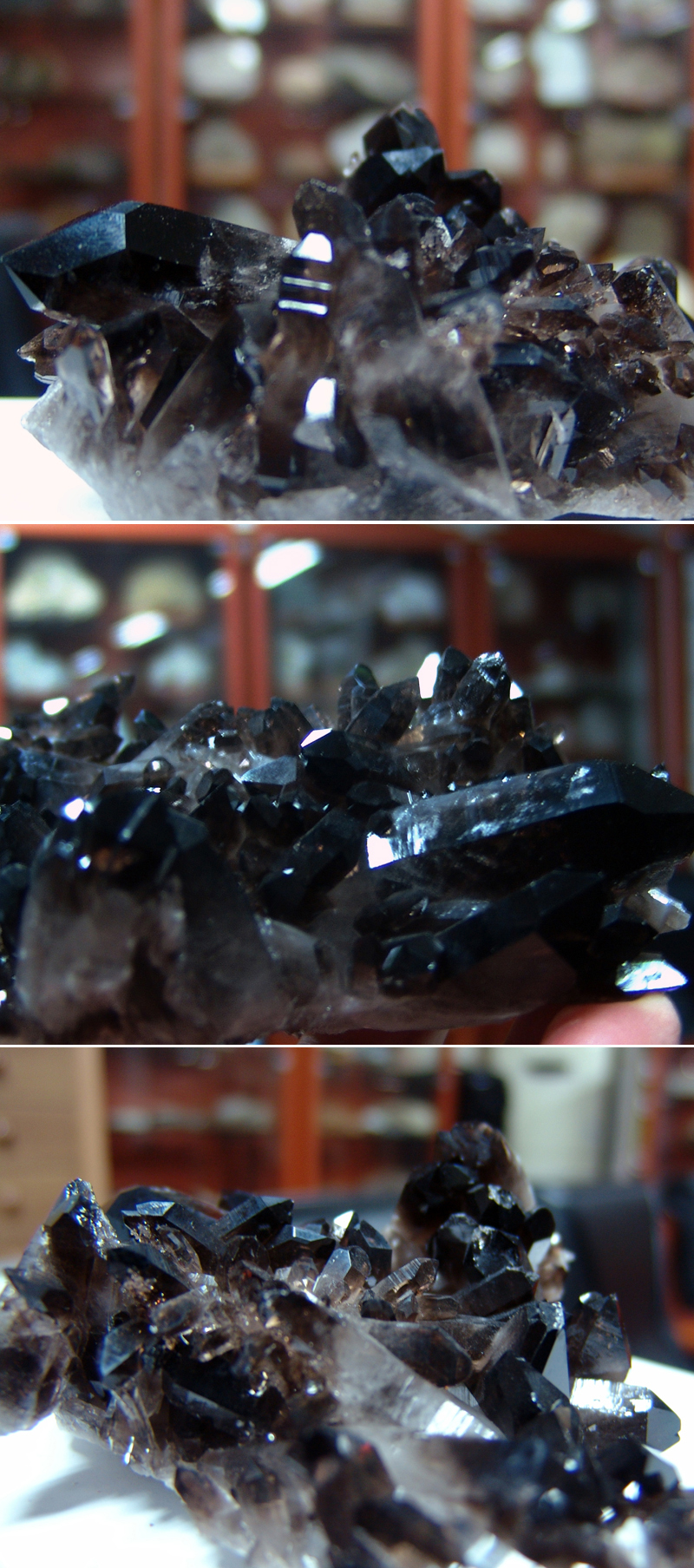
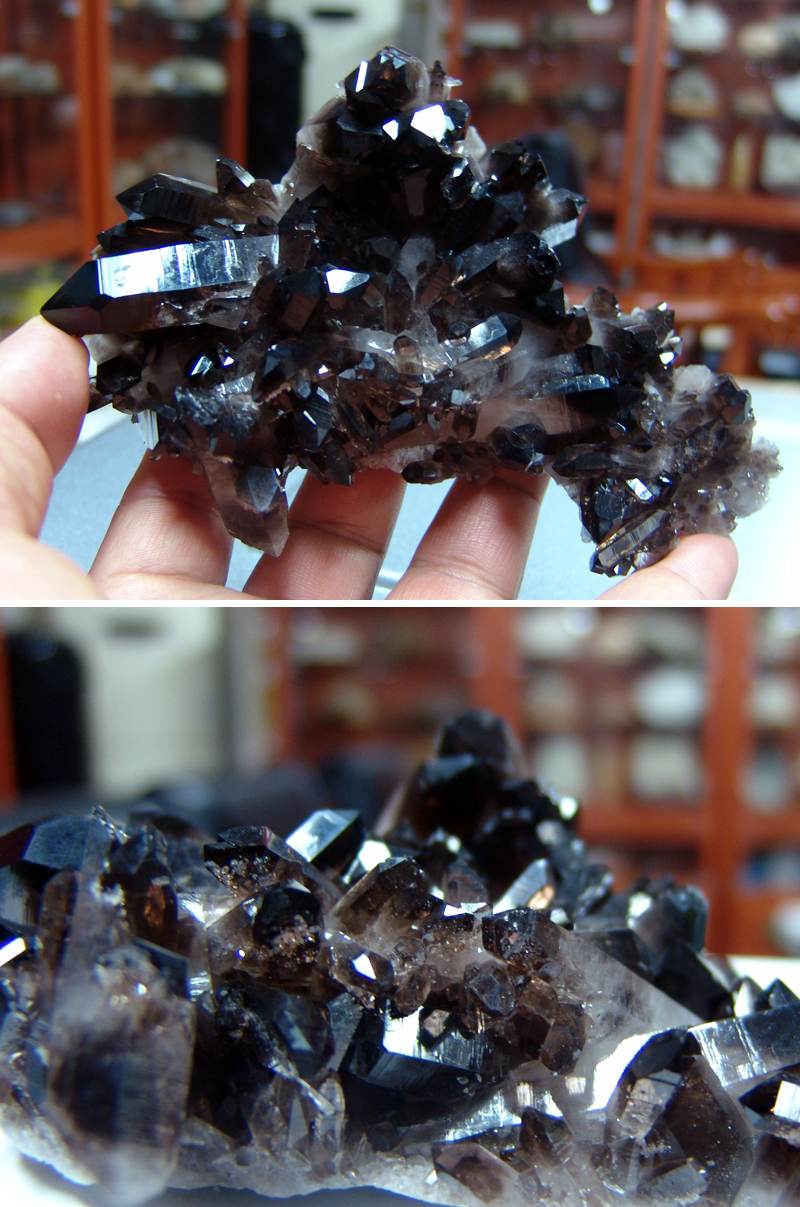
연수정 Quartz (Smoky) 120404-02 

| 국내/해외배송 | |
|---|---|
| 배송비 방법 | 택배 |
| 배송비 | 4,000원 (50,000원 이상 구매 시 무료) |
| 수량 |
|
| 상품 정보 | 가격 | 삭제 |
|---|---|---|
| [총 상품금액(수량)] 0 (0개) | ||
일반명 : 연수정 Quartz (Smoky)
원산지 : Hot Springs, Arkansas, U.S.A.
◈THE MINERAL SMOKY QUARTZ (연수정)
화학명(SiO2), 분류명(Silicate-규산염), 사용처(보석원석 및 장식용 돌), 색상(흑색, 갈색 등), 광택(유리광택), 투명도(반투명 및 투명), 결정계(육방정계), 경도(7.0), 비중(2.65), 조흔색(흰색), 관련광물( Elbaite, Wolframite, Pyrite, Rutile, Zeolites, Fluorite, Calcite, Gold, Hematite, Spodumene 등), 다른특징(열처리를 하면 탈색되는 특징이 있다.), 주산출지(Brazil, Uraguay, Mexico, Russia, Canada, U.S.A 등.)
♠설명 : 석영(Quartz)의 매우 흔한 변종으로 보석의 원석으로는 특이한 색을 가지고 있으며, 풍부하게 산출되기 때문에 자수정(Amethyst)이나 황수정(Citrine)에 비해 가치가 상대적으로 낮다. 때론 황수정(Citrine)으로 판매되기도 하는데 그 이유는 열처리를 하면 탈색이 되면서 황색으로 변하기 때문이다. 스코트랜드에서는 인기 있는 장식석으로 인기 있는 원석이다.
Dims: 145 x 95 x 45 mm
This specimen consists of what some people call "morion(흑수정)", which is Smoky Quartz that has a thoroughly black color. This particular piece was harvested as rock crystal and then treated with x-rays to give it its black coloration. Though there are many crystals in this cluster that are damaged or incomplete, most are in very good condition, with excellent crystal form and clean faces and edges that show off their vitreous luster.
THE MINERAL QUARTZ
· Chemistry: SiO2 , Silicon dioxide
· Class: Silicates
· Subclass: Tectosilicates
· Group: Quartz
· Uses: silica for glass, electrical components, optical lenses, abrasives, gemstones, ornamental stone, building stone, etc.
The Physical Properties of Quartz.
Quartz is the most common mineral on the face of the Earth. It is found in nearly every geological environment and is at least a component of almost every rock type. It frequently is the primary mineral, >98%. It is also the most varied in terms of varieties, colors and forms. This variety comes about because of the abundance and widespread distribution of quartz. A collector could easily have hundreds of quartz specimens and not have two that are the same due to the many broad catagories. The specimens could be separated by answers to the following questions: color?, shade?, pyramidal?, prismatic?, druzy?, twinned?, sceptered?, phantomed?, included?, tapered?, coated?, microcrystalline?, stalactitic?, concretionary?, geoidal?, banded?, etc. Multiple combinations of these could produce hundreds of unique possibilities.
Some macrocrystalline (large crystal) varieties are well known and popular as ornamental stone and as gemstones.
· Amethyst is the purple gemstone variety.
· Citrine is a yellow to orange gemstone variety that is rare in nature but is often created by heating Amethyst.
· Milky Quartz is the cloudy white variety.
· Prasiolite is a leek-green gemstone variety that is rare in nature but is created by heating Amethyst from certain locations.
· Rock crystal is the clear variety that is also used as a gemstone.
· Rose quartz is a pink to reddish pink variety.
· Smoky quartz is the brown to gray variety.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
· Color is as variable as the spectrum, but clear quartz is by far the most common color followed by white or cloudy (milky quartz). Purple (Amethyst), pink (Rose Quartz), gray or brown to black (Smoky Quartz) are also common. Cryptocrystalline varieties can be multicolored.
· Luster is glassy to vitreous as crystals, while cryptocrystalline forms are usually waxy to dull but can be vitreous.
· Transparency: Crystals are transparent to translucent, cryptocrystalline forms can be translucent or opaque.
· Crystal System is trigonal; 3 2.
· Crystal Habits are again widely variable but the most common habit is hexagonal prisms terminated with a six sided pyramid (actually two rhombohedrons). Three of the six sides of the pyramid may dominate causing the pyramid to be or look three sided. Left and right handed crystals are possible and identifiable only if minor trigonal pyramidal faces are present. Druse forms (crystal lined rock with just the pyramids showing) are also common. Massive forms can be just about any type but common forms include botryoidal, globular, stalactitic, crusts of agate such as lining the interior of a geode and many many more.
· Cleavage is very weak in three directions (rhombohedral).
· Fracture is conchoidal.
· Hardness is 7, less in cryptocrystalline forms.
· Specific Gravity is 2.65 or less if cryptocrystalline. (average)
· Streak is white.
· Other Characteristics: Striations on prism faces run perpendicular to C axis, piezoelectric (see tourmaline) and index of refraction is 1.55.
· Associated Minerals are numerous and varied but here are some of the more classic associations of quartz (although any list of associated minerals of quartz is only a partial list): amazonite a variety of microcline, tourmalines especially elbaite, wolframite, pyrite, rutile, zeolites, fluorite, calcite, gold, muscovite, topaz, beryl, hematite and spodumene.
· Notable Occurrences of amethyst are Brazil, Uraguay, Mexico, Russia, Thunder Bay area of Canada, and some locallities in the USA. For Smoky Quartz; Brazil, Colorado, Scotland, Swiss Alps among many others. Rose Quartz is also wide spread but large quantities come from brazil as do the only large find of Rose Quartz prisms. Natural citrine is found with many amethyst deposits but in very rare quantities. Fine examples of Rock crystal come from Brazil (again), Arkansas, many localities in Africa, etc. Fine Agates are found in, of course, Brazil, Lake Superior region, Montana, Mexico and Germany.
· Best Field Indicators are first the fact that it is very common (always assume transparent clear crystals may be quartz), crystal habit, hardness, striations, good conchoidal fracture and lack of good cleavage
















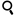 확대보기 및 상세정보
확대보기 및 상세정보